Scientific Image Gallery
Welcome to our Scientific Image Gallery. Here you can find real-life examples of cell images, mostly (but not only) from peripheral blood films, that illustrate typical morphologic characteristics pointing to specific conditions or disorders. This constitutes their diagnostic value.
Click on an image to enlarge it and display a short description.
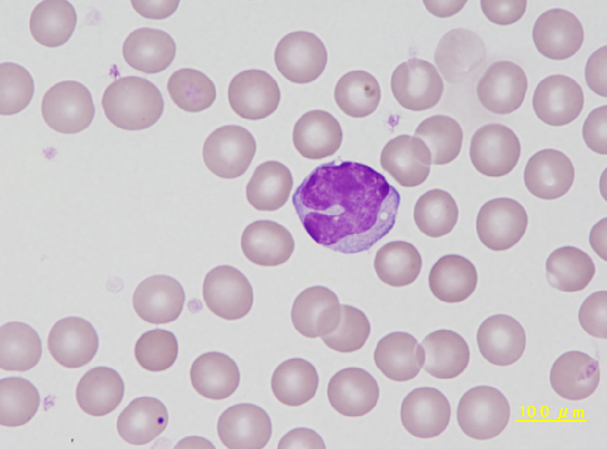
Mononuclear leucocyte containing an inclusion body composed of glycoprotein, a so called Kurloff body. Foa-Kurloff or simply Kurloff cells are unique to the guinea pig and account for up to 4% of the differential leukocyte count. They are reported to have NK cell activity.
<p>Mononuclear leucocyte containing an inclusion body composed of glycoprotein, a so called Kurloff body. Foa-Kurloff or simply Kurloff cells are unique to the guinea pig and account for up to 4% of the differential leukocyte count. They are reported to have NK cell activity. </p>
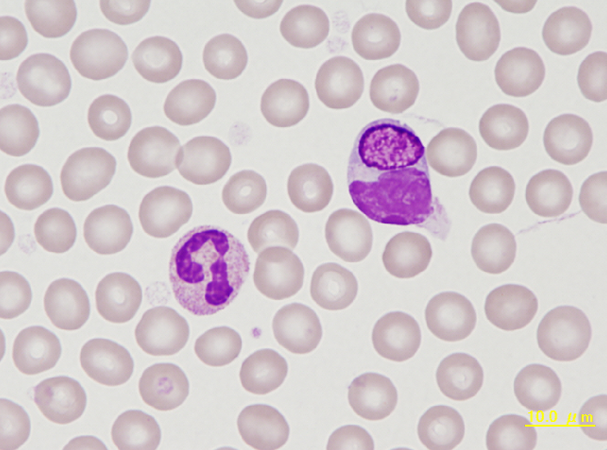
Kurloff cells (KC) are unique to the guinea pig and account for up to 4% of the differential leukocyte
count. The KC cell is a specialized mononuclear leukocyte that contains an intracytoplasmic, finely
granular to fibrillar inclusion body consisting of a mucopolysaccharide. The exact origin and function of these cells is unknown, although it has been speculated that they have killer cell activity.
<p>Kurloff cells (KC) are unique to the guinea pig and account for up to 4% of the differential leukocyte </p> <p>count. The KC cell is a specialized mononuclear leukocyte that contains an intracytoplasmic, finely </p> <p>granular to fibrillar inclusion body consisting of a mucopolysaccharide. The exact origin and function of these cells is unknown, although it has been speculated that they have killer cell activity. </p>
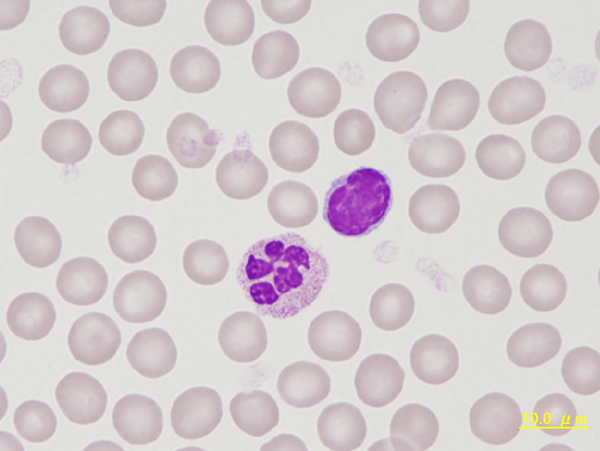
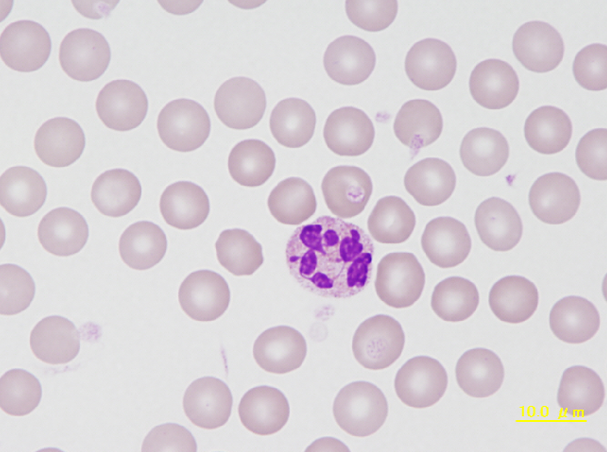
A small lymphocyte with a round to oval, condensed nucleus surrounded by a narrow band of cytoplasm. The neutrophil is hypersegmented, something that is frequently found in guinea pigs. Due to the reddish staining granules this cell is also called heterophil in this species.
<p>A small lymphocyte with a round to oval, condensed nucleus surrounded by a narrow band of cytoplasm. The neutrophil is hypersegmented, something that is frequently found in guinea pigs. Due to the reddish staining granules this cell is also called heterophil in this species. </p>
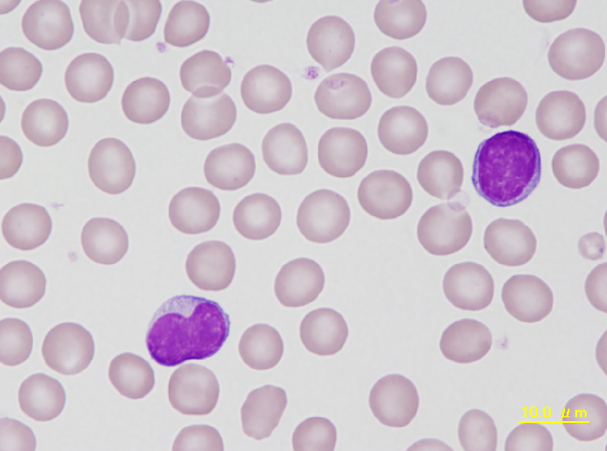
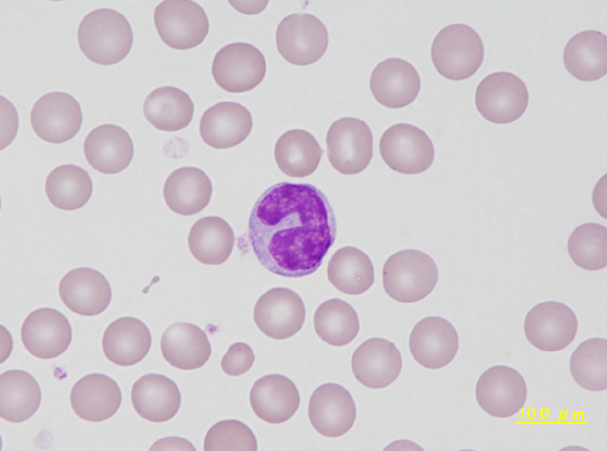
Although the cell to the left has a concave nucleus, its cytoplasm and uniformly staining nuclear chromatin is characteristic for a lymphocyte. The cell to the right is a typical lymphocyte of a guinea pig.
<p>Although the cell to the left has a concave nucleus, its cytoplasm and uniformly staining nuclear chromatin is characteristic for a lymphocyte. The cell to the right is a typical lymphocyte of a guinea pig.</p>

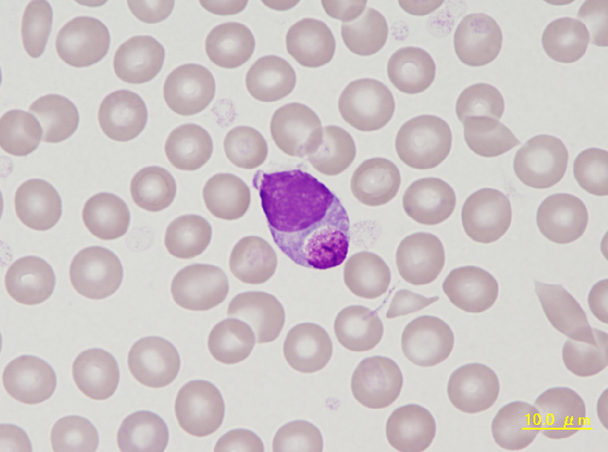
Cell description:
Size: larger than normal lymphocytes
Nucleus: round, oval, dumbbell-shaped or bilobed with little chromatin condensation and sometimes indistinct nucleolus
Cytoplasm: abundant weakly basophilic with irregular “hairy” margins
<p>Cell description: </p> <p>Size: larger than normal lymphocytes </p> <p>Nucleus: round, oval, dumbbell-shaped or bilobed with little chromatin condensation and sometimes indistinct nucleolus </p> <p>Cytoplasm: abundant weakly basophilic with irregular “hairy” margins</p>

Hairy cell from a hairy cell leukaemia. Typical are the monocytic type nuclei with loose chromatin, and the grey-blue, heterogeneous cytoplasm. The hairy protrusions may be missing in some cases.
<p>Hairy cell from a hairy cell leukaemia. Typical are the monocytic type nuclei with loose chromatin, and the grey-blue, heterogeneous cytoplasm. The hairy protrusions may be missing in some cases.</p>