Scientific Image Gallery
Welcome to our Scientific Image Gallery. Here you can find real-life examples of cell images, mostly (but not only) from peripheral blood films, that illustrate typical morphologic characteristics pointing to specific conditions or disorders. This constitutes their diagnostic value.
Click on an image to enlarge it and display a short description.
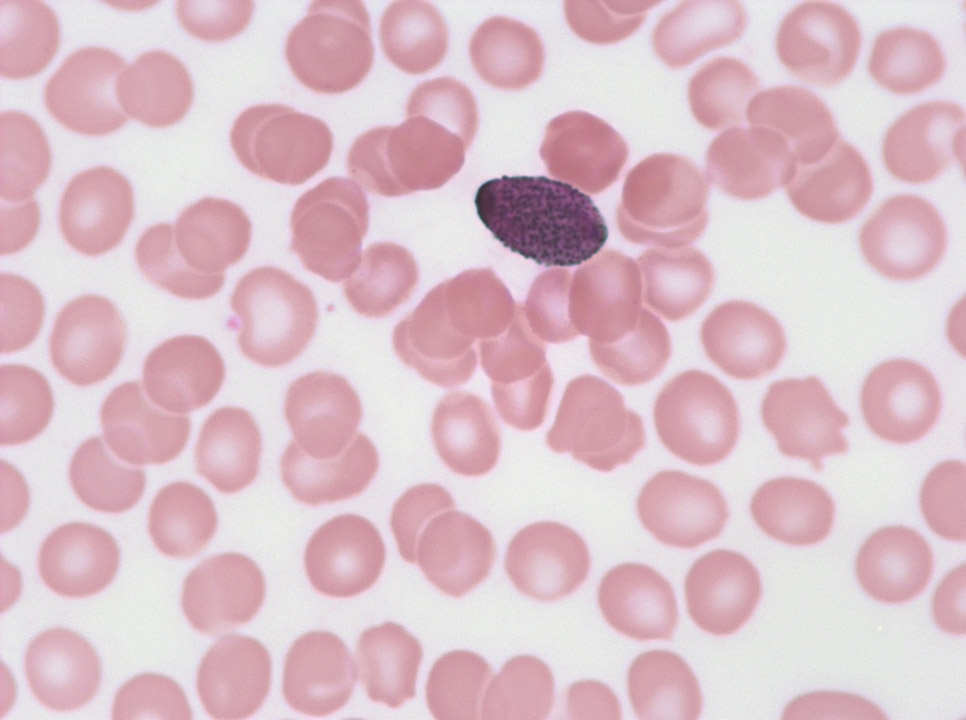
In primary myelofibrosis (PMF, also called chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis, CIMF) nuclei of megakaryocytes can be detected in the peripheral blood (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain) and rarely, like here, small megakaryocytes. Both derive from extramedullary haematopoiesis.
<p>In primary myelofibrosis (PMF, also called chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis, CIMF) nuclei of megakaryocytes can be detected in the peripheral blood (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain) and rarely, like here, small megakaryocytes. Both derive from extramedullary haematopoiesis.</p>
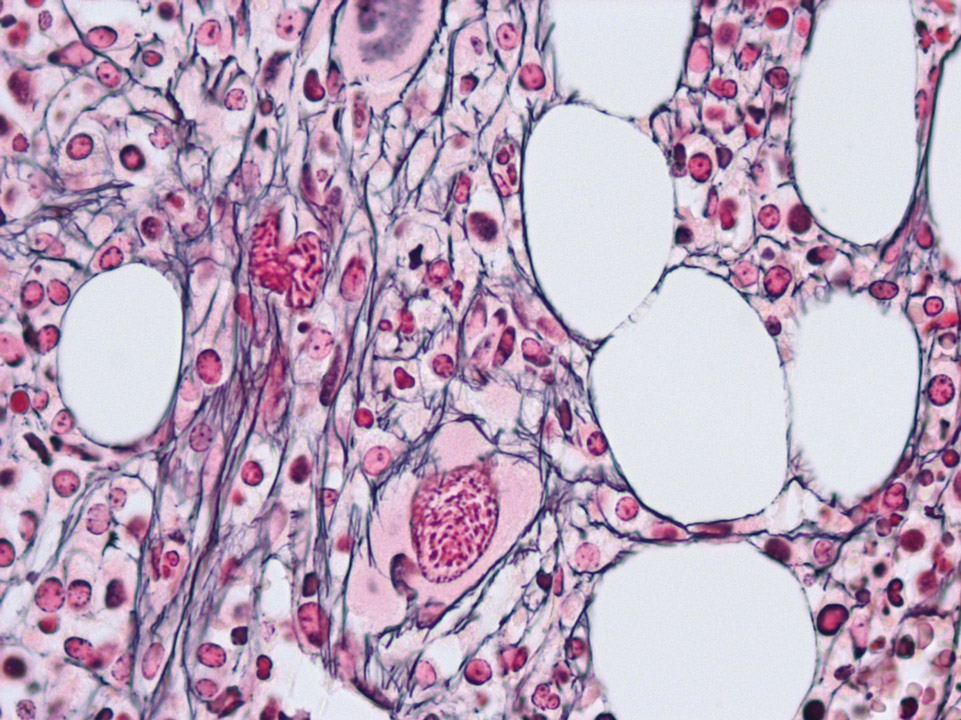
In the bone marrow histology the reticular fibres in PMF (alo called CIMF) can be identified by their black colour (Gomori stain).
<p>In the bone marrow histology the reticular fibres in PMF (alo called CIMF) can be identified by their black colour (Gomori stain). </p>
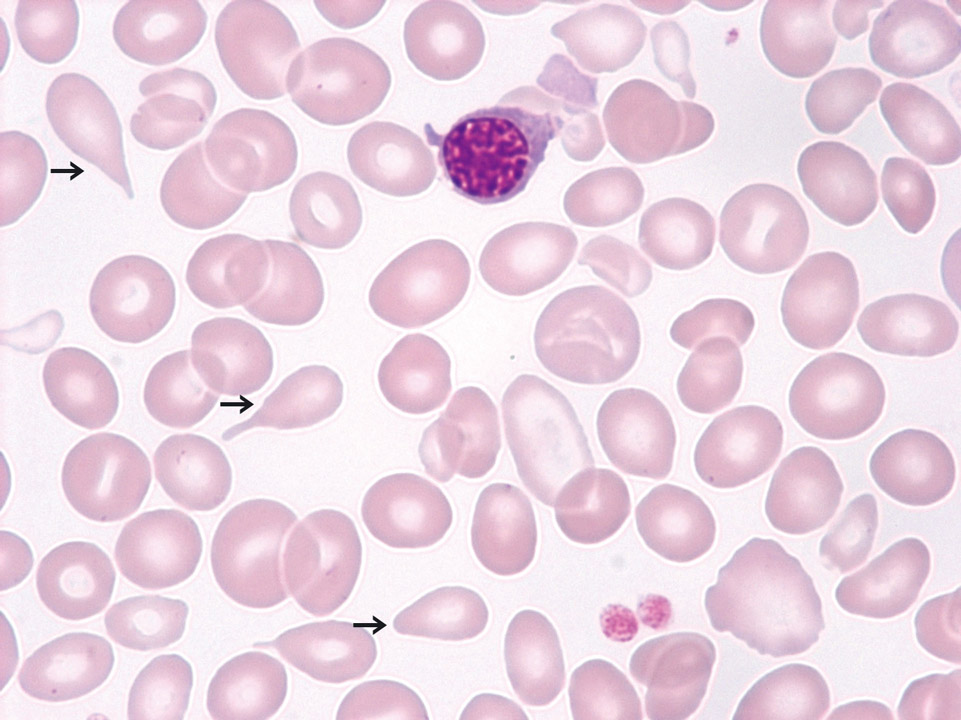
PMF (also called CIMF) in the fibrotic stage with a leucoerythroblastic blood picture (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain): In this patient immature granulocytes, erythroblasts and many teardrop cells (->) were found. In the fibrotic stage there is usually anaemia present and a low to normal or reduced platelet count. Myeloblasts might be present. But more than 10% already indicate blast cell excess or transition into AML.
<p>PMF (also called CIMF) in the fibrotic stage with a leucoerythroblastic blood picture (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain): In this patient immature granulocytes, erythroblasts and many teardrop cells (->) were found. In the fibrotic stage there is usually anaemia present and a low to normal or reduced platelet count. Myeloblasts might be present. But more than 10% already indicate blast cell excess or transition into AML. </p>
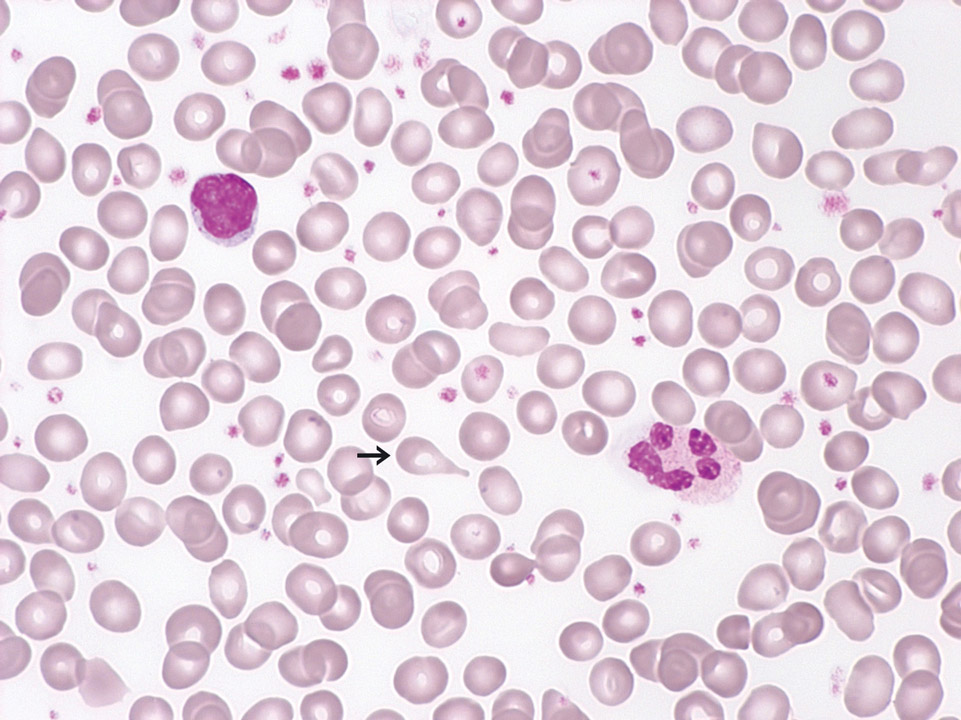
This peripheral blood film (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain) is from a patient with PMF (also called CIMF) in the prefibrotic stage. You can see scattered teardrop cells (->). Furthermore, a few granulocytic precursors and very few erythroblasts were detected (not shown). The automated cell count showed slight leukocytosis, thrombocytosis and anaemia.
<p>This peripheral blood film (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain) is from a patient with PMF (also called CIMF) in the prefibrotic stage. You can see scattered teardrop cells (->). Furthermore, a few granulocytic precursors and very few erythroblasts were detected (not shown). The automated cell count showed slight leukocytosis, thrombocytosis and anaemia.</p>
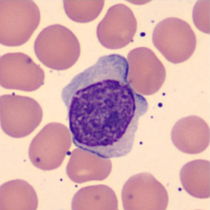
Cell description:
Size: 10-18 µm, smaller than lymphoblast
Nucleus: round with coarser structure than a lymphoblast, one distinct nucleolus
Cytoplasm: blue without granules
<p>Cell description: </p> <p>Size: 10-18 µm, smaller than lymphoblast </p> <p>Nucleus: round with coarser structure than a lymphoblast, one distinct nucleolus </p> <p> Cytoplasm: blue without granules </p>
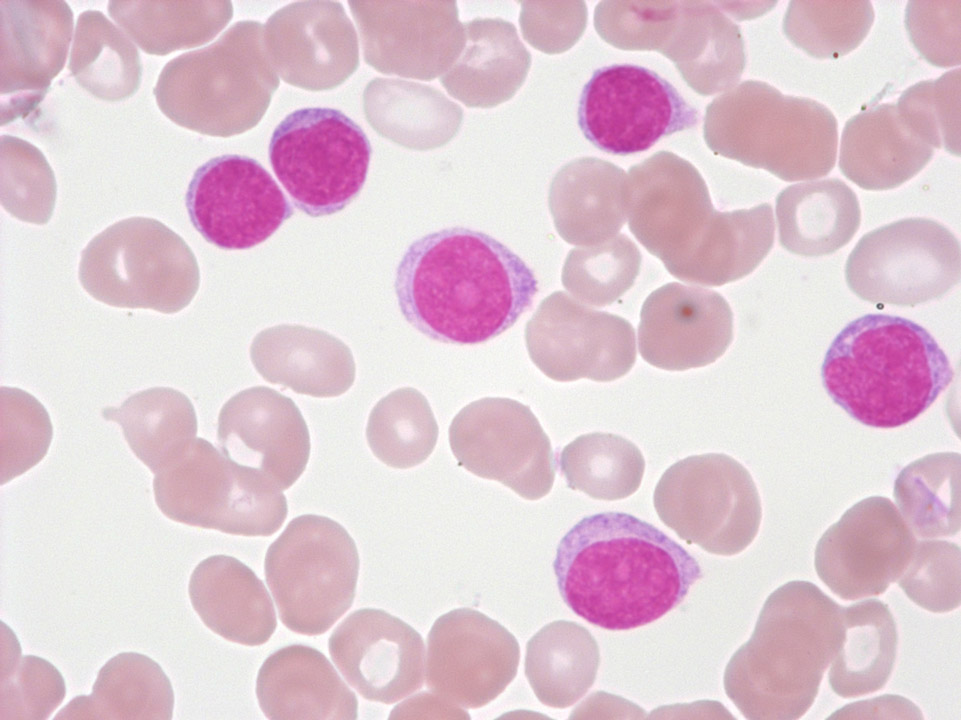
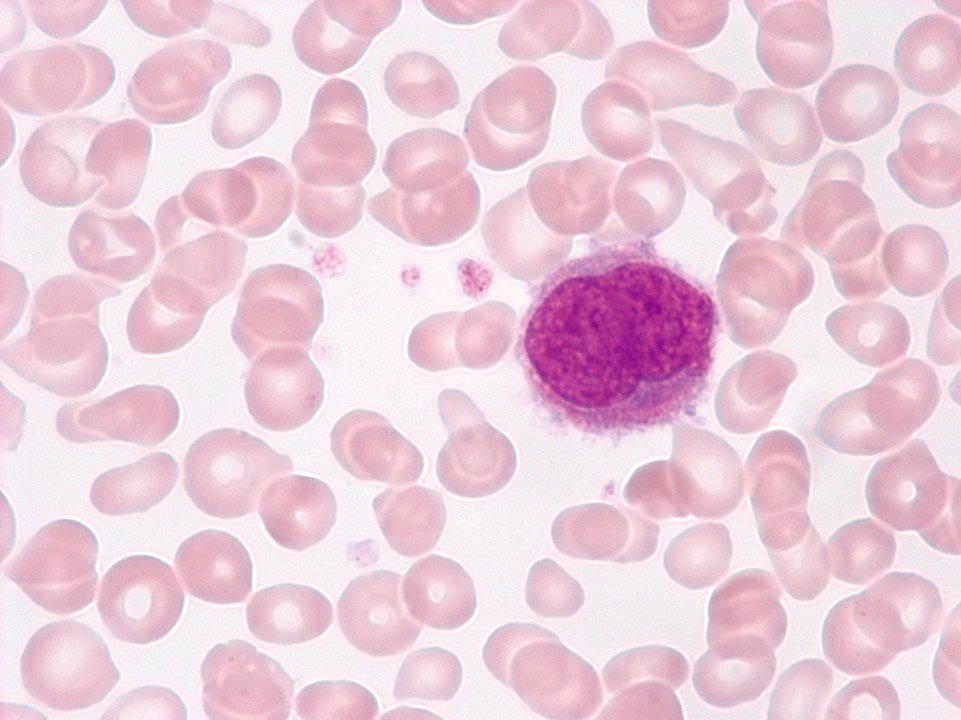
EDTA blood of a female patient with a transitional form of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia/prolymphocytic leukaemia. The three large cells are prolymphocytes, the smaller ones are lymphocytes.
<p>EDTA blood of a female patient with a transitional form of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia/prolymphocytic leukaemia. The three large cells are prolymphocytes, the smaller ones are lymphocytes.</p>
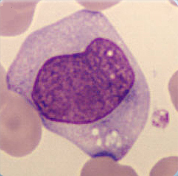
Cell description:
Size: bigger than monoblast
Nucleus: oval, kidney-shaped or lobulated, diffuse chromatin pattern, sometimes with nucleoli
Cytoplasm: pale basophil with fine azurophil granula.
Cell division is still possible.
<p>Cell description: </p> <p>Size: bigger than monoblast </p> <p>Nucleus: oval, kidney-shaped or lobulated, diffuse chromatin pattern, sometimes with nucleoli </p> <p>Cytoplasm: pale basophil with fine azurophil granula. </p> <p>Cell division is still possible.</p>
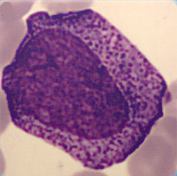
Cell description:
Size: 15-25 µm
Nucleus: oval with identifiable nucleoli and diffuse chromatin structure Cytoplasm: basophilic with visible golgi-zone and eye-catching azurophil granula (primary granulation)
<p>Cell description: </p> <p>Size: 15-25 µm </p> <p>Nucleus: oval with identifiable nucleoli and diffuse chromatin structure Cytoplasm: basophilic with visible golgi-zone and eye-catching azurophil granula (primary granulation)</p>